10 results found for: “War_in_Ukraine”.
Request time (Page generated in 0.6227 seconds.)Russian invasion of Ukraine
Last Update: 2024-06-09T17:44:54Z Word Count : 35248Russo-Ukrainian War
Last Update: 2024-06-01T18:36:48Z Word Count : 24917List of wars involving Ukraine
Last Update: 2024-06-07T19:21:38Z Word Count : 1746War in Donbas
Last Update: 2024-06-06T00:46:19Z Word Count : 36617Casualties of the Russo-Ukrainian War
Last Update: 2024-06-09T15:08:23Z Word Count : 17060War crimes in the Russian invasion of Ukraine
Last Update: 2024-06-02T04:07:39Z Word Count : 24161Ukrainian–Soviet War
Last Update: 2024-05-09T14:17:35Z Word Count : 3676List of military aid to Ukraine during the Russo-Ukrainian War
Last Update: 2024-06-08T19:56:01Z Word Count : 22323Ukrainian War of Independence
Last Update: 2024-05-24T11:59:07Z Word Count : 3989
Main result
Russian invasion of Ukraine
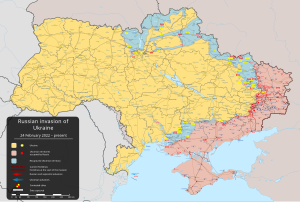 On 24 February 2022, Russia invaded Ukraine in an escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War that started in 2014. The invasion became the largest attack on a European country since World War II. It is estimated to have caused tens of thousands of Ukrainian civilian casualties and hundreds of thousands of military casualties. By June 2022, Russian troops occupied about 20% of Ukraine. From a population of 41 million, about 8 million Ukrainians had been internally displaced and more than 8.2 million had fled the country by April 2023, creating Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. Extensive environmental damage caused by the war has been widely described as an ecocide. War-related disruption to Ukrainian agriculture and transport contributed to a food crisis worldwide. The Russian attacks on civilians, causing mass civilian casualties and displacement, have been characterised by scholars as genocide and democide against Ukrainians.
Before the invasion, Russian troops massed near Ukraine's borders as Russian officials denied any plans to attack. Russian president Vladimir Putin then announced a "special military operation", saying it was to support the Russian-backed breakaway republics of Donetsk and Luhansk, whose paramilitary forces had been fighting Ukraine in the Donbas conflict since 2014. Putin espoused irredentist views challenging Ukraine's right to exist, and falsely claimed that Ukraine was governed by neo-Nazis persecuting the Russian minority. He said his goal was to "demilitarise and denazify" Ukraine. Russian air strikes and a ground invasion were launched at a northern front from Belarus towards Kyiv, a southern front from Crimea, and an eastern front from the Donbas and towards Kharkiv. Ukraine enacted martial law, ordered a general mobilisation and severed diplomatic relations with Russia.
Russian troops retreated from the northern front by April 2022 after encountering logistical challenges and stiff Ukrainian resistance. On the southern and southeastern fronts, Russia captured Kherson in March and Mariupol in May after a destructive siege. Russia launched a renewed offensive in the Donbas and continued to bomb military and civilian targets far from the front line, including the energy grid through the winter. In late 2022, Ukraine launched successful counteroffensives in the south and east. Soon after, Russia announced the illegal annexation of four partly-occupied regions. In November, Ukraine retook parts of Kherson Oblast, including Kherson city. In June 2023, Ukraine launched another counteroffensive in the southeast, which by the end of the year had petered out with only small amounts of territory retaken.
The invasion was met with widespread international condemnation. The United Nations General Assembly passed a resolution condemning the invasion and demanding a full Russian withdrawal in March 2022. The International Court of Justice ordered Russia to suspend military operations and the Council of Europe expelled Russia. Many countries imposed sanctions on Russia and its ally Belarus, and provided humanitarian and military aid to Ukraine. The Baltic states all declared Russia a terrorist state. Protests occurred around the world, with anti-war protesters in Russia being met by mass arrests and the enactment of a law enabling greater media censorship. Over 1,000 companies closed their operations in Russia and Belarus as a result of the invasion. The International Criminal Court (ICC) opened investigations into possible crimes against humanity, war crimes, abduction of children, and genocide. The ICC issued four arrest warrants in that regard: for Putin and Maria Lvova-Belova in March 2023, alleging responsibility for the unlawful deportation of children, as well as for commanders Sergey Kobylash and Viktor Sokolov in 2024, for alleged war crimes.
On 24 February 2022, Russia invaded Ukraine in an escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War that started in 2014. The invasion became the largest attack on a European country since World War II. It is estimated to have caused tens of thousands of Ukrainian civilian casualties and hundreds of thousands of military casualties. By June 2022, Russian troops occupied about 20% of Ukraine. From a population of 41 million, about 8 million Ukrainians had been internally displaced and more than 8.2 million had fled the country by April 2023, creating Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. Extensive environmental damage caused by the war has been widely described as an ecocide. War-related disruption to Ukrainian agriculture and transport contributed to a food crisis worldwide. The Russian attacks on civilians, causing mass civilian casualties and displacement, have been characterised by scholars as genocide and democide against Ukrainians.
Before the invasion, Russian troops massed near Ukraine's borders as Russian officials denied any plans to attack. Russian president Vladimir Putin then announced a "special military operation", saying it was to support the Russian-backed breakaway republics of Donetsk and Luhansk, whose paramilitary forces had been fighting Ukraine in the Donbas conflict since 2014. Putin espoused irredentist views challenging Ukraine's right to exist, and falsely claimed that Ukraine was governed by neo-Nazis persecuting the Russian minority. He said his goal was to "demilitarise and denazify" Ukraine. Russian air strikes and a ground invasion were launched at a northern front from Belarus towards Kyiv, a southern front from Crimea, and an eastern front from the Donbas and towards Kharkiv. Ukraine enacted martial law, ordered a general mobilisation and severed diplomatic relations with Russia.
Russian troops retreated from the northern front by April 2022 after encountering logistical challenges and stiff Ukrainian resistance. On the southern and southeastern fronts, Russia captured Kherson in March and Mariupol in May after a destructive siege. Russia launched a renewed offensive in the Donbas and continued to bomb military and civilian targets far from the front line, including the energy grid through the winter. In late 2022, Ukraine launched successful counteroffensives in the south and east. Soon after, Russia announced the illegal annexation of four partly-occupied regions. In November, Ukraine retook parts of Kherson Oblast, including Kherson city. In June 2023, Ukraine launched another counteroffensive in the southeast, which by the end of the year had petered out with only small amounts of territory retaken.
The invasion was met with widespread international condemnation. The United Nations General Assembly passed a resolution condemning the invasion and demanding a full Russian withdrawal in March 2022. The International Court of Justice ordered Russia to suspend military operations and the Council of Europe expelled Russia. Many countries imposed sanctions on Russia and its ally Belarus, and provided humanitarian and military aid to Ukraine. The Baltic states all declared Russia a terrorist state. Protests occurred around the world, with anti-war protesters in Russia being met by mass arrests and the enactment of a law enabling greater media censorship. Over 1,000 companies closed their operations in Russia and Belarus as a result of the invasion. The International Criminal Court (ICC) opened investigations into possible crimes against humanity, war crimes, abduction of children, and genocide. The ICC issued four arrest warrants in that regard: for Putin and Maria Lvova-Belova in March 2023, alleging responsibility for the unlawful deportation of children, as well as for commanders Sergey Kobylash and Viktor Sokolov in 2024, for alleged war crimes.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
